How to List Servers in an Active Directory Domain
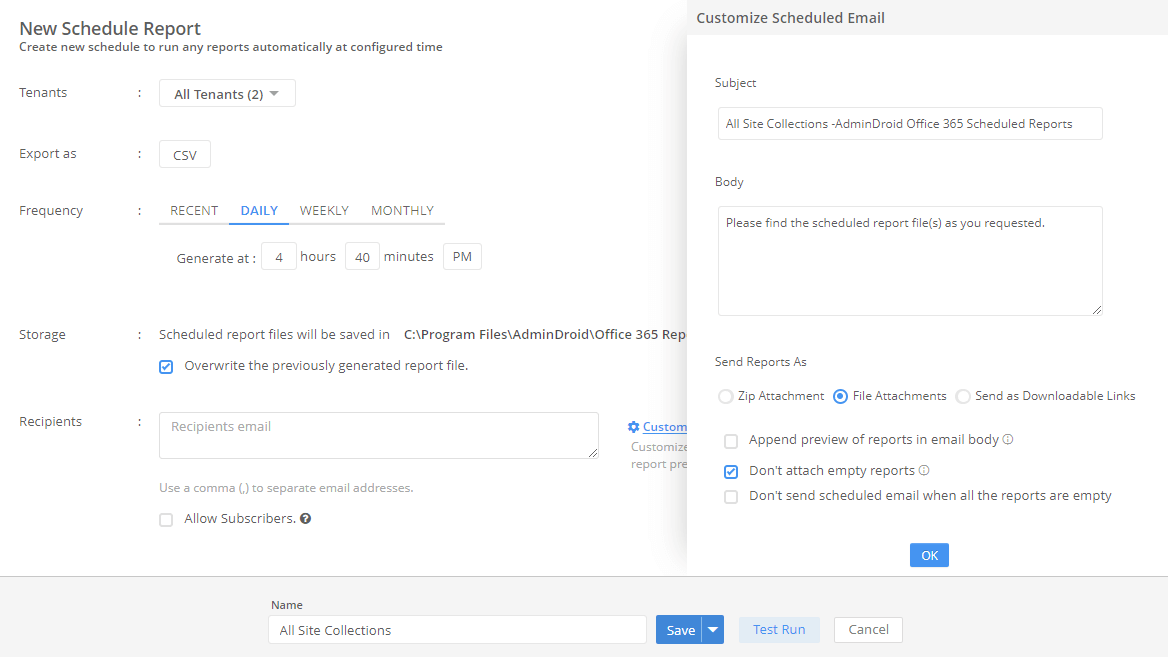
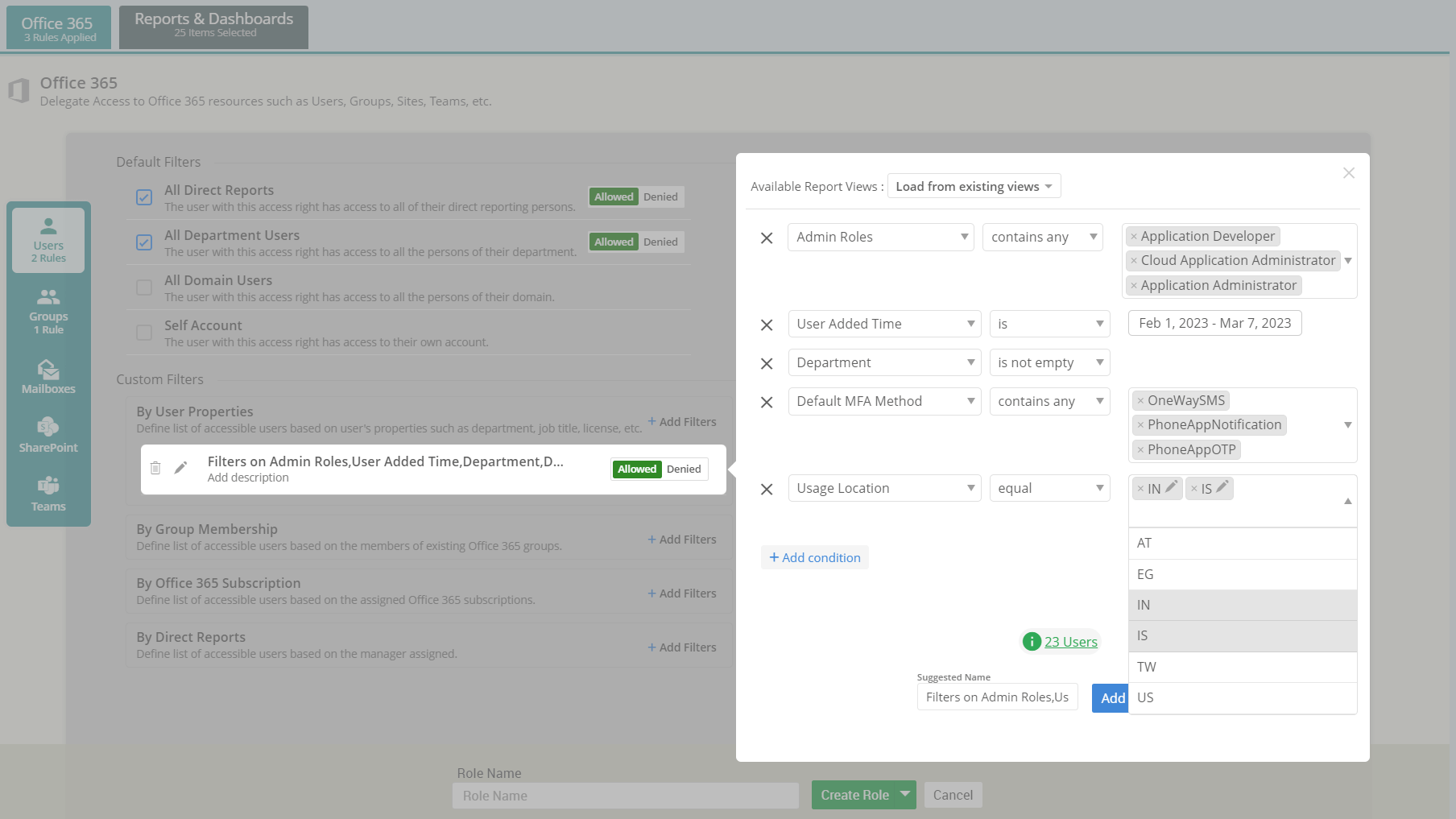
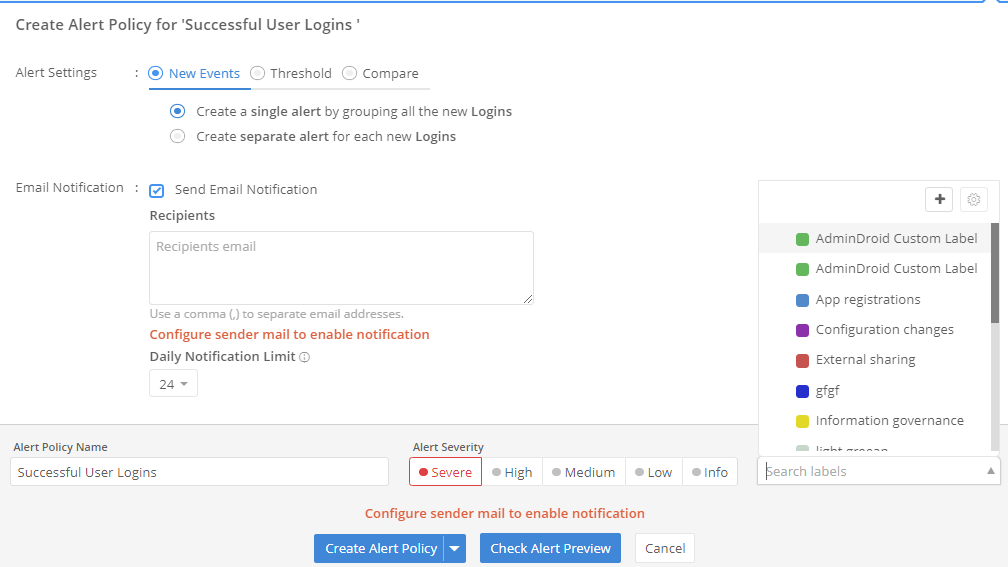
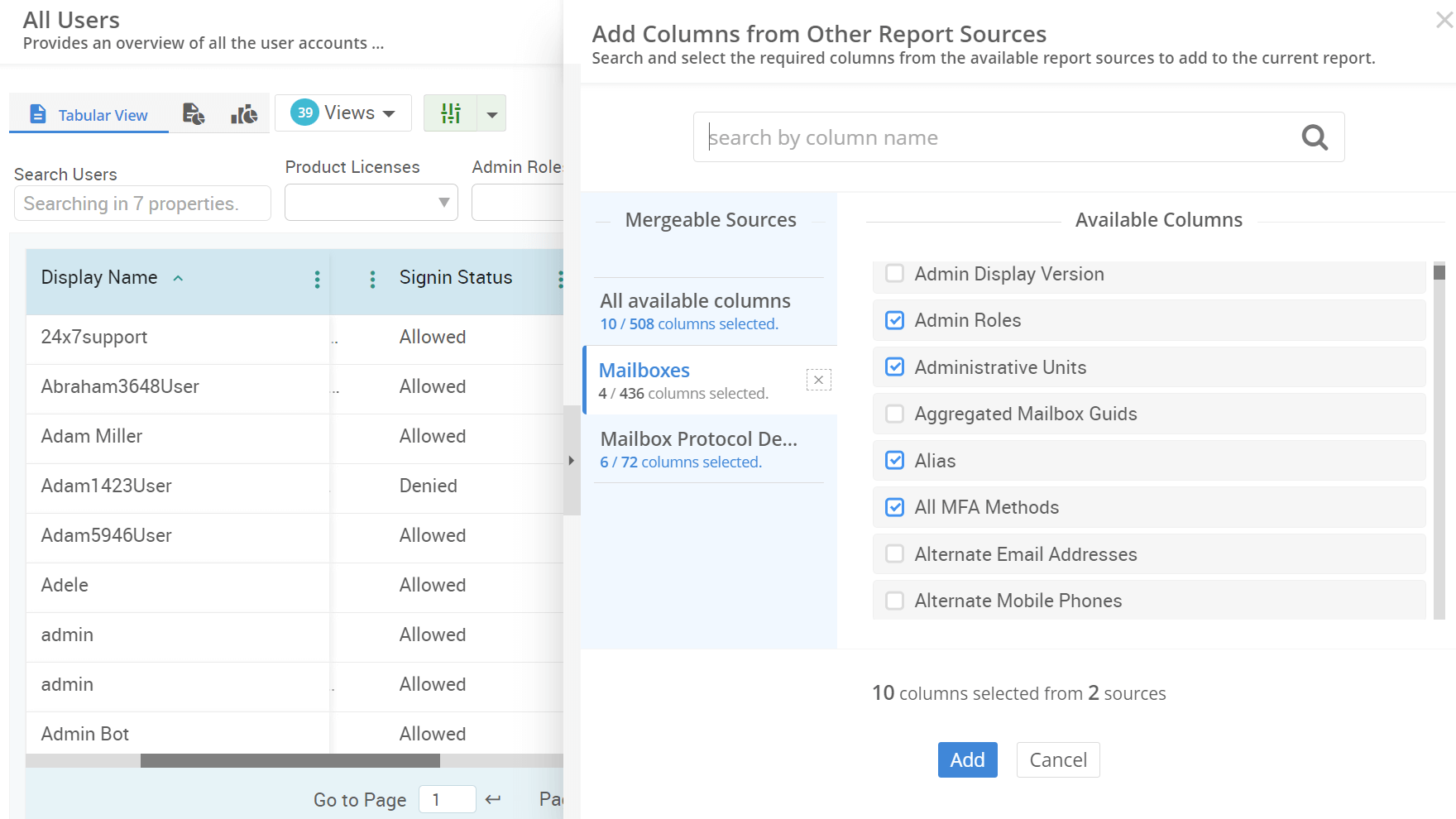
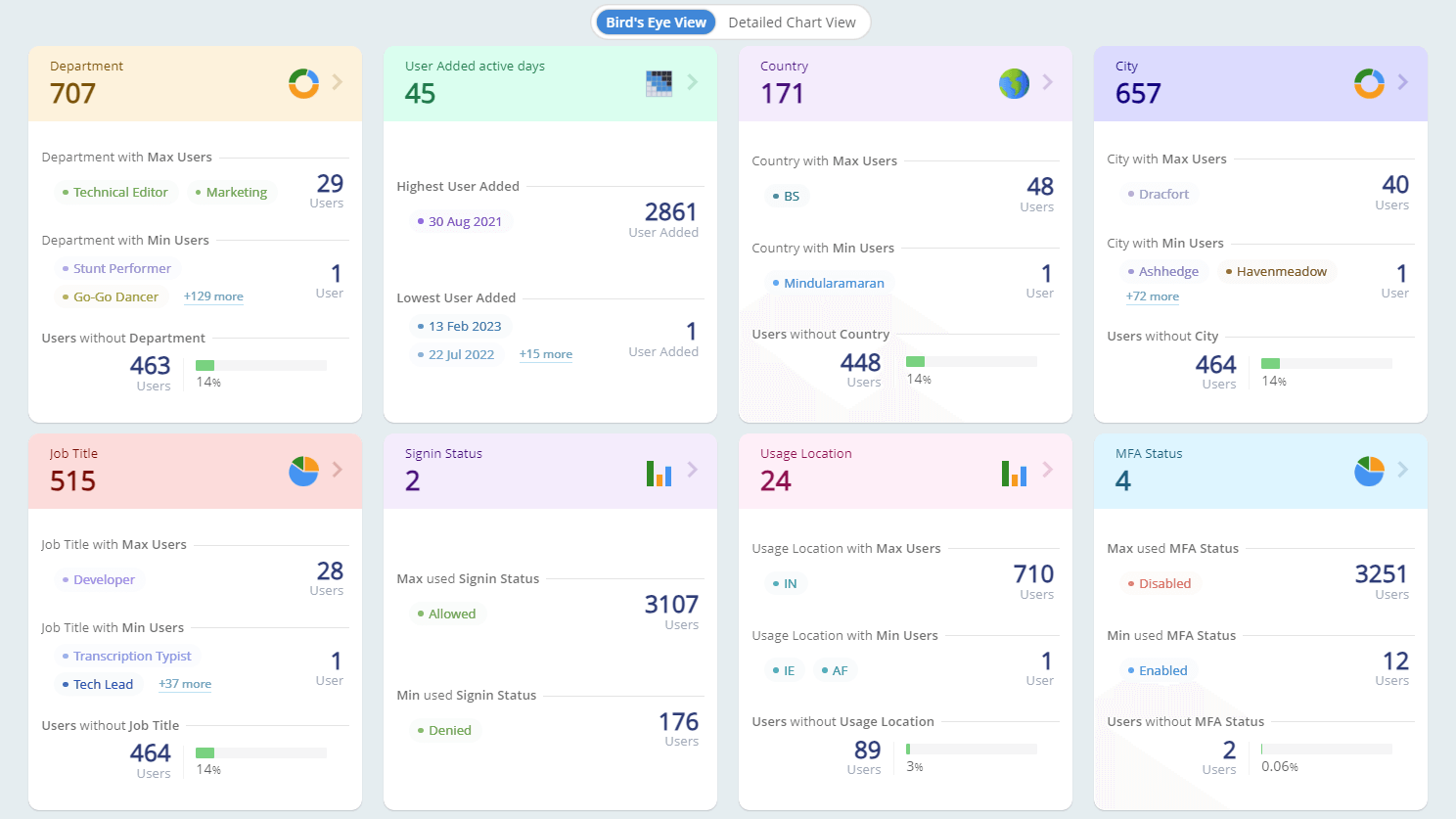
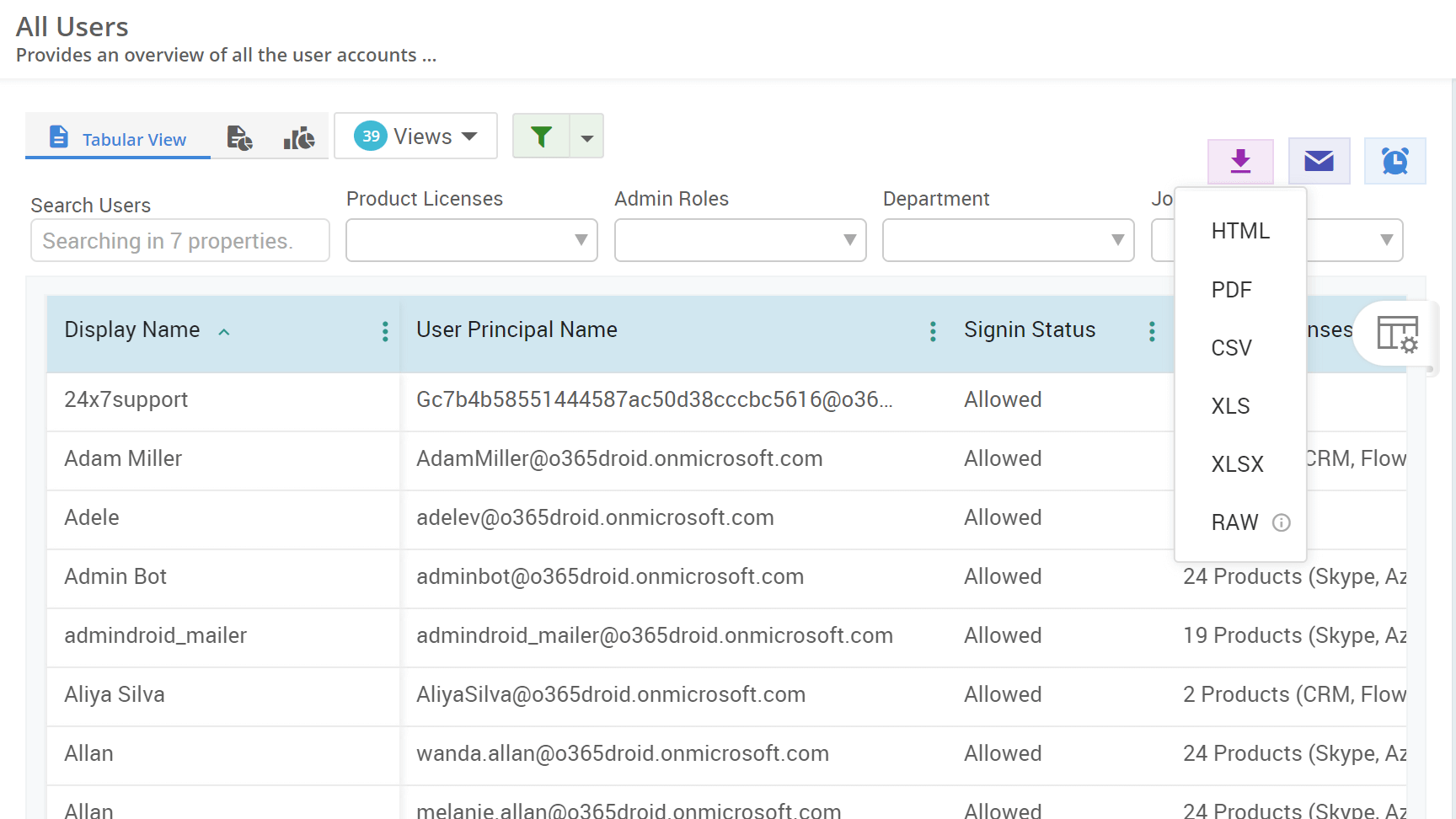
An up-to-date list of Active Directory servers in the domain is essential for effective IT management. It allows administrators to keep track of the infrastructure, ensure backup resources, improve security, and enhance overall directory performance. This guide will walk you through the steps to find all servers in an Active Directory domain and lay a strong foundation for further server management tasks.