How to Audit Administrative Units in Microsoft 365
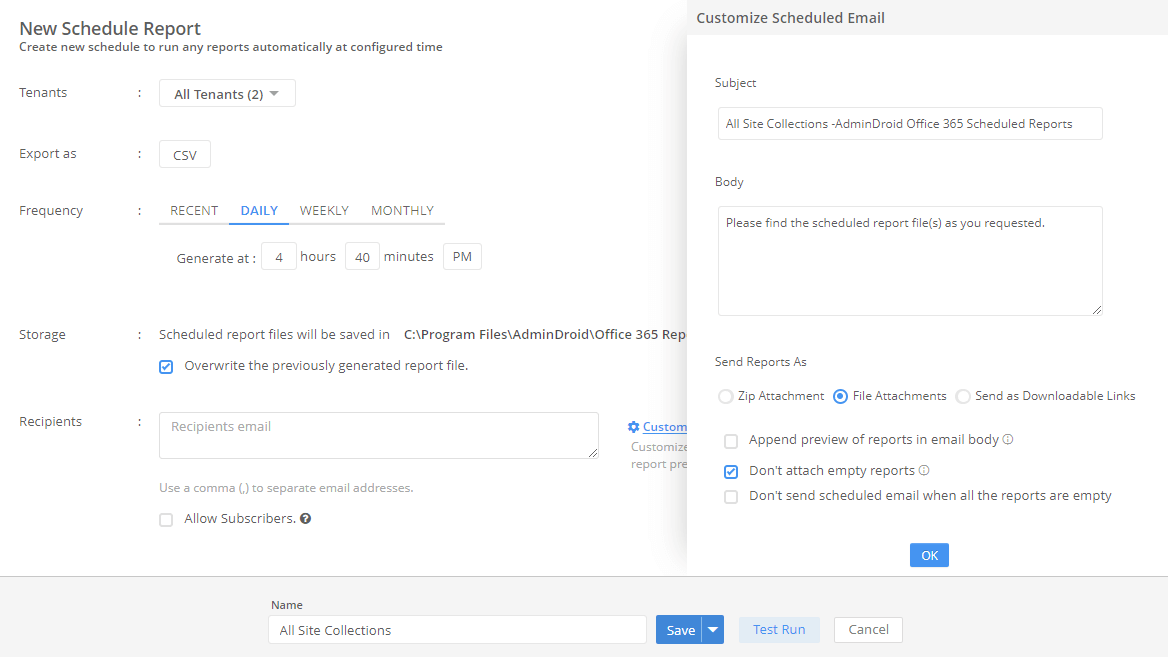
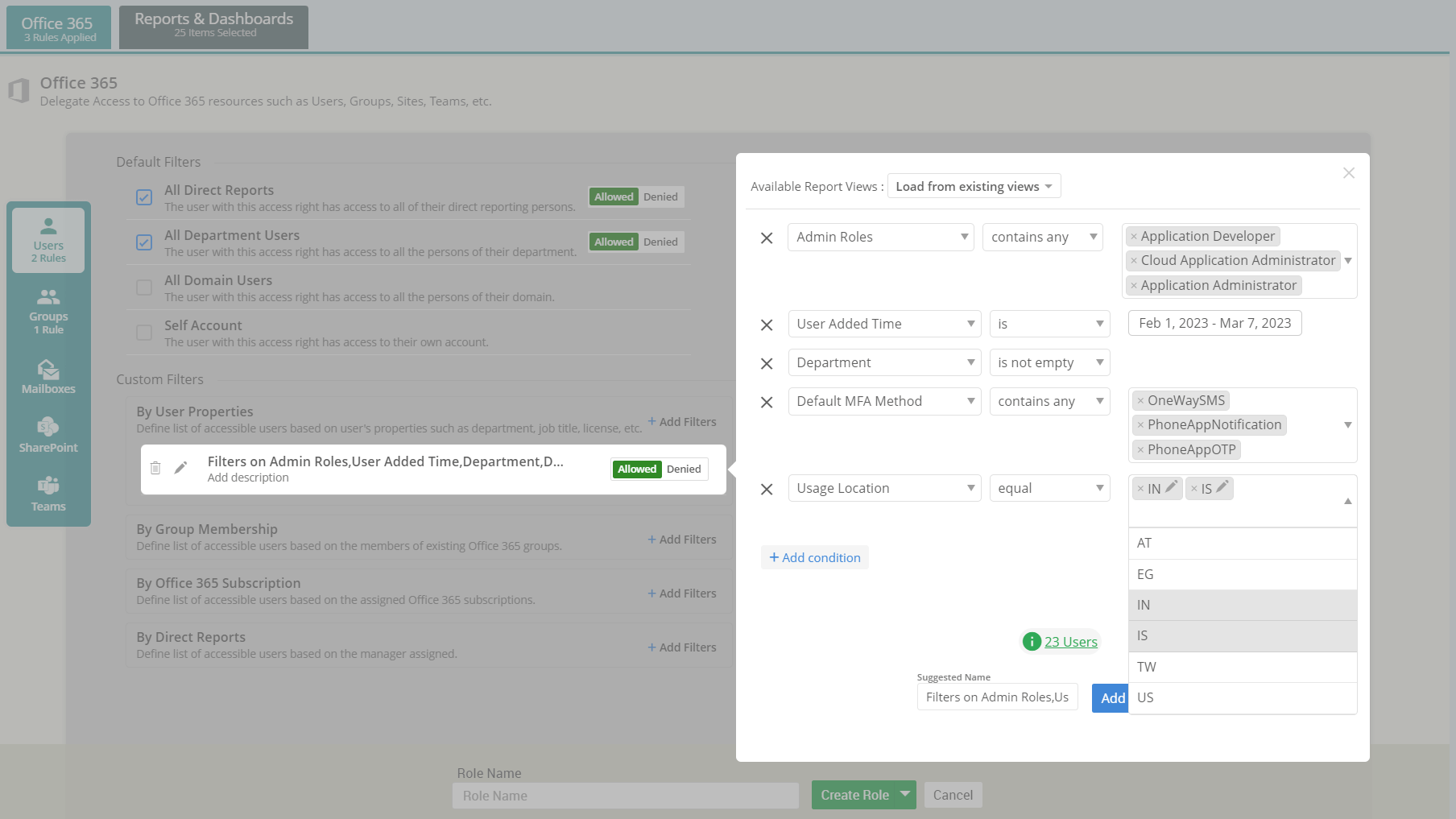
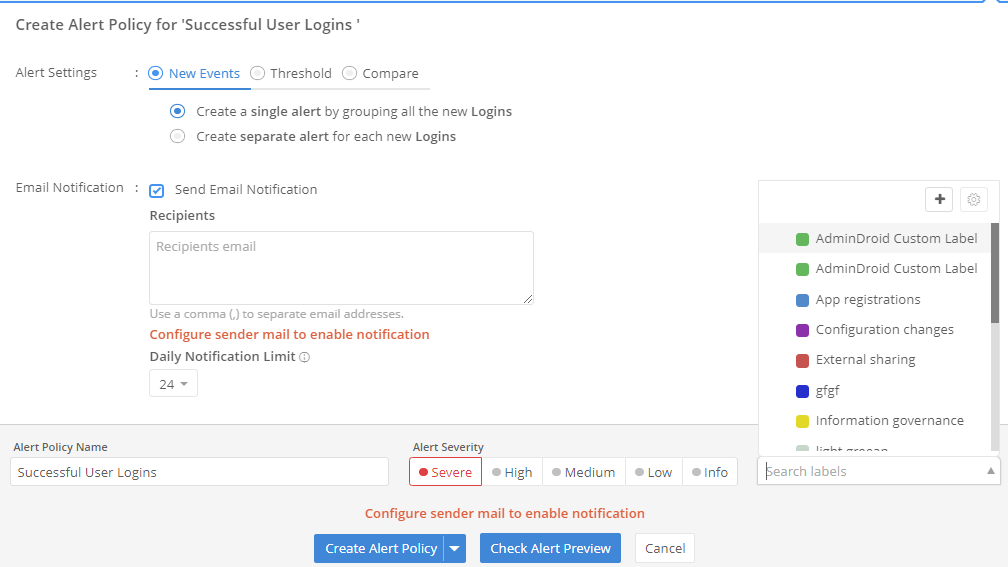
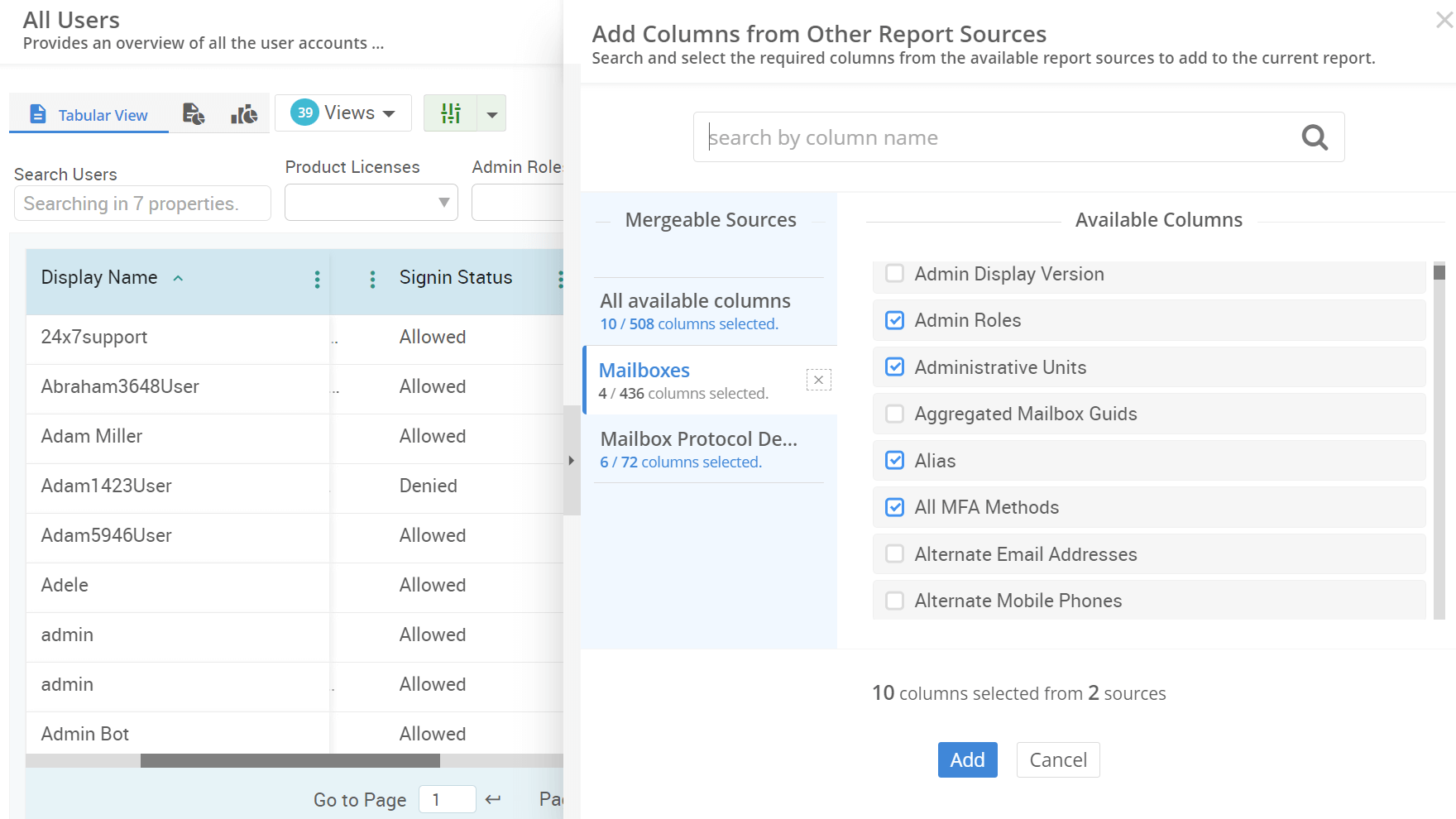
Is managing user permissions in Microsoft 365 becoming overwhelming? Administrative units (AUs) help to streamline access management across departments and roles. Thus, auditing AUs is crucial for maintaining security and compliance to ensure that only authorized users access sensitive resources. This guide offers efficient methods to audit administrative units which enhance access control and reduce security risks in your organization.